GREENWAT
Project name:
“Carbonaceous materials from wastes – proficient tools for water decontamination”
Funded by: UEFISCDI – Executive Unit for Financing Higher Education, Research, Development and Innovation (UEFISCDI)
5.1 – IDEI Program – Exploratory Research Projects
Contract no. 83PCE/01.07.2025
Project coordinator: NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY POLITEHNICA BUCHAREST – UNSTPB
UNSTPB Project Director: Prof. Dr. Habil. Chem. Ecaterina Matei
Project value: 1,147,368 lei
Project value from other sources: 0 lei
Implementation duration: 36 months (2025–2028)
Project objective:
The project is based on the three principles of the circular economy: (i) elimination of waste and pollution, (ii) redesign of products and/or materials using the 3R concept (reduce, recycle, reuse), and (iii) conservation of natural resources. Various types of waste will be transformed into valuable materials used as adsorbents, ion exchangers, or photocatalysts for the removal of water pollutants (EP and HM). This project helps to minimize waste quantities by transforming vegetable and industrial waste into eco-friendly carbon magnetic materials with nanostructures (GREENWAT materials).
SUMMARY
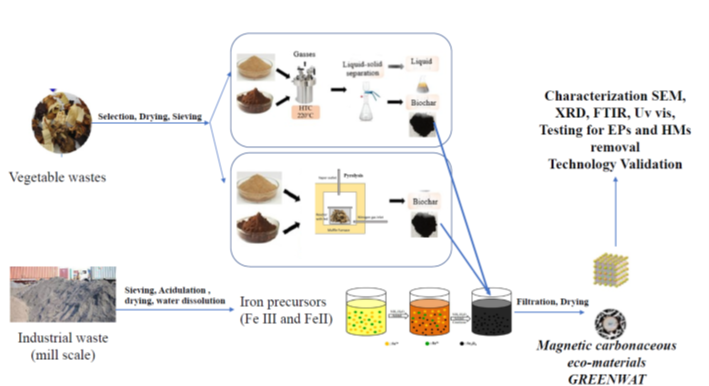
The steps developed with this project are (i) obtaining GREENWAT eco-materials used water decontamination from two valuable types of wastes: vegetables resulted from intensive consumption (such as such as nuts shells, sunflower husk, vineyard pomace, banana peels) and metallurgical waste (mill scale) (ii) characterization and validation of the new class of eco-materials, (iii) selective removal capacity of new obtained eco-materials for inorganic and organic contaminants.
Green synthesis will be used to obtain: (i) firstly, carbonaceous eco-materials by 2 thermochemical treatments (hydrothermal HTC and pyrolysis) using vegetables wastes such as nuts shells, sunflower husk, vineyard pomace, banana peels and (ii) secondly, the final magnetic carbonaceous eco-materials GREENWAT by loading iron precursors from a metallurgical waste (mills scale) processing onto carbonaceous materials.
PROJECT TEAM
| 1. Prof. Habil. Ecaterina Matei Senior Researcher |
| Coordinates the project implementation and all researches’ activities; vegetable and industrial waste processing and magnetic carbonaceous GREENWAT obtaining and testing, data analysis. Scientific and dissemination activities. |
| 2. CS I Habil. Maria RÂPĂ Senior Researcher |
| The tasks will be in vegetable and industrial testing of physical and chemical properties (ATR-FTIR, UV-VIS), chromatographic and TOC analysis for EPs, HTC treatment for wastes, protocols elaborations, dissemination activities |
| 3. Prof. Cristian Predescu Senior Researcher |
| Resposible for quality tests; pyrolisys method applied to the wastes, data analyses, research reports. |
| 4. Assoc. Prof Andrei Contantin BERBECARU Senior Researcher |
| The tasks will be in material characterization (SEM-EDS) and dissemination activities. |
| 5. Prof. Mirela Gabriela SOHACIU, Senior Researcher |
| The tasks will be in protocols elaboration for industrial wastes processing, research reports. |
| 6. Assoc. Prof. Habil. Andra Mihaela PREDESCU Postdoctoral Researcher |
| Responsible for industrial mill scale processing, characterization, testing for HMs removal, after magnetic carbonaceous materials obtaining, dissemination activities. |
| 7. Lect. George COMAN Postdoctoral Researcher |
| The tasks will be in pyrolysis treatment and optical cahracterizations of eco-materials, data analysis. |
| 8. Lect. Claudia Ionela TARCEA Postdoctoral Researcher |
| Specialist in catalytic degradation processes, dissemination activities. |
| 9. Dr. Chem. Andreea Anca ȘĂULEAN (ȚURCANU), Postdoctoral Researcher |
| Specialist in advanced wastewater treatment (adsorption processes), atomic absorption spectrometry analysis for HMs, HTC processes applied for wastes. |
STAGE 1 – Deliverables achieved, according to the project proposal:
D1. WP1 interim research report including: D1.1. Protocols for obtaining GREENWAT hydrocarbons using plant waste as precursors; D1.2. Protocols for the synthesis of GREENWAT magnetic eco-materials; D1.3. Characterization protocols; D1.4. Identification and removal protocols for organic pollutants and heavy metals. 1 article accepted for publication
Result indicators:
4 working protocols
5 types of hydrocarbons from coffee grounds (HTC1…5)
5 types of HTC activated with NaOH (HTC1….5)
50% HTC yield
2 articles published, rated Q1 and Q2
1 participation in an international conference.
Dissemination of results:
- Râpă, M.; Alhalaili, B.; Dinca, F.; Predescu, A.; Matei, E.; Vidu, R. Hybrid Electrospun Conductive Nanofibers for Emerging Organic Contaminants’ Degradation in Visible Light Photocatalysis: A Review. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR SCIENCES 2025, 26, doi:10.3390/ijms26189055. Impact factor 4.9 (Q1)
- Popescu, A.; Matei, E.; Badiceanu, A.; Balint, A.; Rapa, M.; Coman, G.; Predescu, C. An Optimistic Vision for Public Transport in Bucharest City After the Bus Fleet Upgrades. ENVIRONMENTS 2025, 12, doi:10.3390/environments12070242. Impact factor 3.7 (Q2)
- Râpă, M1, Matei, E1, Predescu, C.1, Matić, M2, Kosić, D. Challenges, experimental approach, and prospects into microplastics waste management. 13th INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING AND MANAGEMENT, Empower Sustainability 17 – 20 September 2025, Iasi, Romania (oral presentation).
COGNITIVE AND SOCIO-ECONOMIC IMPACT
The importance of the theme is given by the design of magnetic carbonaceous eco-materials obtained from vegetal and industrial wastes as proficient tool in emerging pollutants (EPs) and heavy metals (HMs) removal processes resulted from water and wastewaters. This approach is based on the 3 principles of circular economy: (i) eliminate waste and pollution, (ii) re-design products and/or materials using 3R concept (reduction, recycling, reuse), and (iii) save the natural resources . Different wastes could be converted into valuable materials used as further as adsorbents, ion exchangers or photocatalysts for water pollutants (EPs and HMs) removal. This project helps in waste quantities minimization by converting of vegetable and industrial wastes into magnetic carbonaceous eco-materials with nanostructures (GREENWAT materials). Green synthesis will be used to obtain: (i) firstly, carbonaceous eco-materials by 2 thermochemical treatments (hydrothermal HTC and pyrolysis) using vegetables wastes such as nuts shells, sunflower husk, vineyard pomace, banana peels and (ii) secondly, the final magnetic carbonaceous eco-materials GREENWAT by loading iron precursors from a metallurgical waste (mills scale) processing onto carbonaceous materials.